What is Suicide?
What is Suicide?
“Suicide is a serious public health problem that can have lasting harmful effects on individuals, families, and communities. There are many factors that contribute to suicide. The goal of suicide prevention is to reduce factors that increase risk and increase factors that promote resilience.”
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Suicide is a death caused by injuring oneself with an intent to die. It is highly prevalent both in the United States and worldwide.
What Groups are Most Impacted?
In 2020, suicide was the second leading cause of death for youth ages 10–14 years and the third leading cause for youth ages 15–24 years.
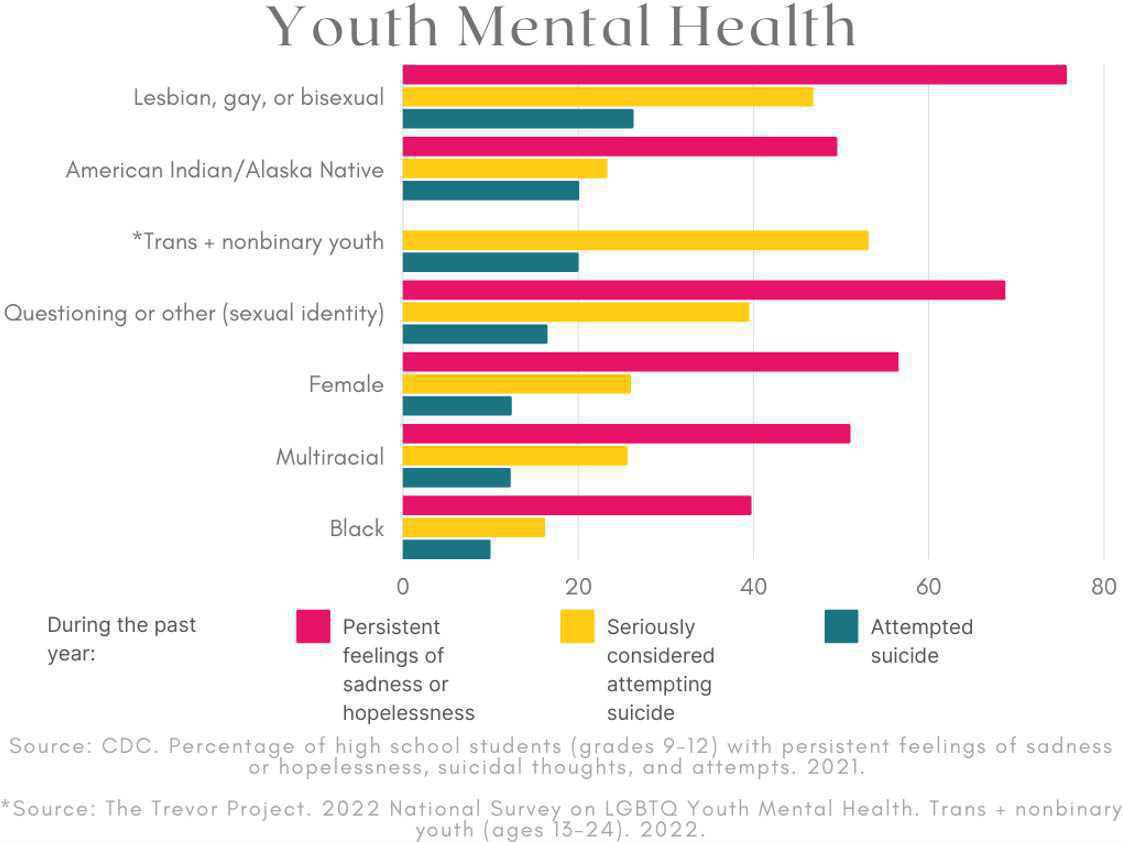
Data collected by the CDC demonstrates that youth from traditionally underserved and marginalized backgrounds and identities, including LGBTQ2SIA+ youth, Black youth, and American Indian/Alaska Native youth experience higher suicide rates than their peers. Research has found that factors including racism, historical trauma, and systemic inequities likely contribute to these higher rates.
The graph below demonstrates percentages of youth from traditionally underserved and marginalized communities who experienced persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness, seriously considered attempting suicide, or attempted suicide during a school year.
“Suicide occurs in response to multiple biological, psychological, interpersonal, environmental, and societal influences that interact with one another, often over time. Belonging, safety, dignity, and hope can support resilience and healing for individuals and communities, and protect against suicide.”
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)